Lithium batteries have revolutionized our electronic world, providing powerful and efficient energy solutions that have become integral to modern technology. From smartphones to electric vehicles, lithium-ion technology dominates the rechargeable battery market due to its superior lifespan and energy density. However, as we increasingly rely on these batteries, important questions regarding their environmental impact and proper battery disposal emerge. With the push for the Right to Repair, consumers are now more aware of the implications of choosing devices that utilize lithium batteries and the responsibility that comes with them. As we navigate this new landscape, it is essential to consider sustainable practices and informed decisions about our energy sources and their disposal.
As we delve into the realm of modern energy storage, one cannot overlook the remarkable potential of lithium-based energy sources. Known for their light weight and efficiency, these rechargeable power cells are often highlighted for their role in enhancing the functionality of various gadgets, providing more than just basic utility. The discussion surrounding their environmental influence and the principles of the Right to Repair has sparked elaborate debates among consumers and manufacturers alike. Furthermore, the evolution of battery technologies, including alternatives to traditional disposable cells, has encouraged a shift in how we view and manage our electronic devices. It remains crucial to explore innovative solutions for responsible battery use and disposal while recognizing the broader implications of these choices on our planet.
The Rise of Lithium Batteries in Modern Devices
The advent of lithium batteries has transformed the landscape of portable electronics, making devices more efficient and convenient than ever before. Unlike their predecessors, such as alkaline and NiMH batteries, lithium-ion technology offers higher energy density and a longer lifespan. This technological revolution enables everything from smartphones to electric vehicles to operate longer on a single charge, fundamentally altering how we interact with technology in our daily lives.
However, the proliferation of lithium batteries isn’t without its drawbacks. While these batteries provide significant advantages, they also contribute to a growing environmental issue. The rapid turnover of devices powered by lithium batteries can lead to increased waste. Many consumer electronics have transitioned to a disposable model, where once the battery is dead, the entire product is simply discarded. This raises crucial questions about sustainable practices and confronts us with the reality of battery disposal challenges.
Environmental Impact of Lithium-ion Technology
Lithium-ion technology has enabled advancements in energy storage, but it has also created environmental concerns that cannot be overlooked. Mining for lithium, cobalt, and nickel often leads to ecological degradation, water shortages, and pollution of surrounding environments. Furthermore, the production processes involved in manufacturing lithium batteries contribute significantly to carbon emissions, casting a shadow over their utility and prompting discussions about the true sustainability of these technologies.
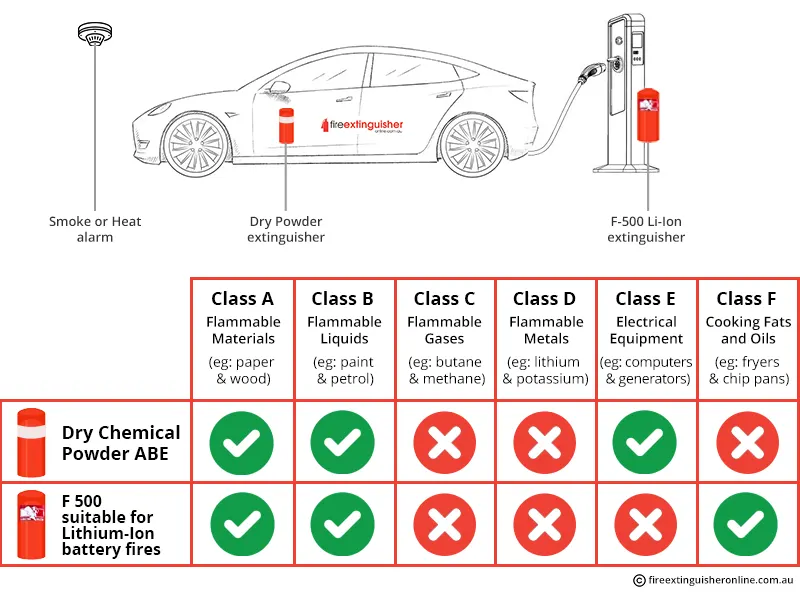
There’s also the impact of battery disposal on our environment. As consumer electronics become increasingly disposable, understanding how to manage and recycle lithium batteries is more crucial than ever. Battery disposal is not just about throwing them away; improper disposal can lead to hazardous waste contaminating soil and waterways. Therefore, it is essential to explore effective recycling methods that not only recapture valuable materials but also minimize environmental harm.
The Right to Repair Movement and Battery Management
The Right to Repair movement is gaining momentum as consumers advocate for more sustainable practices regarding electronic devices, including lithium batteries. As these devices become more ingrained in our lives, many are calling for legislation that mandates easier access to replacement batteries and repair parts. This movement emphasizes the need for design choices that allow users to replace batteries without discarding entire devices, promoting both sustainability and user autonomy.
Implementing Right to Repair principles could significantly extend the lifecycle of products powered by lithium batteries. Encouraging manufacturers to design for repairability can reduce electronic waste by promoting a culture of reuse rather than disposal. This is especially pertinent in a world where rechargeable batteries are becoming the norm in consumer electronics—promoting the idea that if you can easily replace a battery, devices will have greater longevity.
Rechargeable Batteries: The Case for NiMH vs. Lithium-ion
While lithium batteries dominate the market, rechargeable NiMH batteries are making a comeback, especially for household applications. Unlike lithium batteries, which may be more suited for high-energy devices needing quick recharge times, NiMH batteries present a viable option for gadgets like remote controls and flashlights where high-energy output is not as critical. These batteries have evolved significantly and offer a sustainable alternative for consumers seeking an environmentally-friendly choice.
The major highlight of using rechargeable batteries is their reduced environmental impact compared to single-use models. By investing in rechargeable NiMH cells, consumers can enjoy convenience while minimizing waste. Moreover, as awareness about the life cycle of batteries grows, it may lead to a shift in consumer preference, emphasizing sustainable choices over convenience and pushing manufacturers to adopt practices that align with the Right to Repair philosophy.
Standardized Battery Sizes and Consumer Access
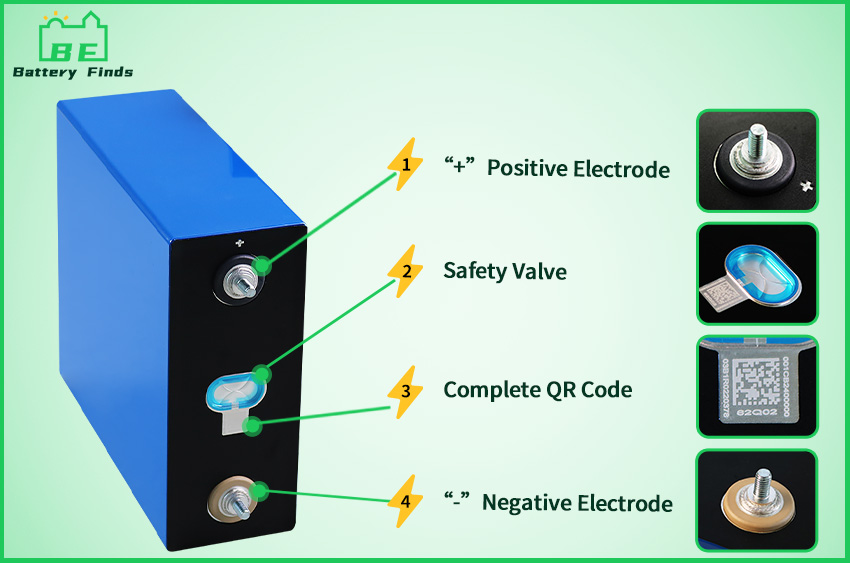
The introduction of standardized pouch and cylindrical lithium cells, such as the 18650 battery, has revolutionized accessibility for consumers and makers alike. These components are not only easier to source but also encourage DIY projects and innovation in the electronic sphere. Their popularity is a testament to the growing community that values adaptability and flexibility in powering devices, thereby enhancing user experience.
However, this standardization comes with its own sets of challenges. While it may improve access to lithium-ion battery technology for custom projects, it also underscores the need for more responsible usage and disposal systems. With the growing market for rechargeable batteries, there is a pressing need for effective recycling programs to manage the end-of-life phase of these batteries, ensuring they don’t contribute to environmental degradation.
Future of Lithium Battery Technology and Regulations
The future of lithium battery technology is closely tied to regulatory developments and consumer expectations. As lawmakers look into potential regulations that could promote battery recycling and renewable sourcing of materials, it is critical for the industry to evolve alongside these guidelines. The anticipated EU regulations focusing on battery production and waste management could set a global precedent, pressuring other regions to adopt more sustainable practices.
Additionally, manufacturers need to consider these emerging regulations when developing new lithium products. By integrating eco-friendly practices into the design process, companies can enhance their reputations and appeal to a growing market of environmentally conscious consumers. This will involve investing in research for more sustainable materials and fostering a manufacturing culture that prioritizes minimal environmental impact.
Innovations in Battery Technology: Beyond Lithium
As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, innovators are exploring alternatives to traditional lithium batteries. From sodium-ion batteries to other innovative technologies, the landscape of energy storage could see a significant shift in the coming years. These alternatives aim to address not only performance but also environmental impact, signaling a potential paradigm shift in how we power our devices sustainably.
Research into these alternative battery technologies is vital. By diversifying the materials and methods used for energy storage, manufacturers can minimize the mining impacts associated with lithium while continuing to provide high-performance energy solutions. This could open the door for more sustainable practices and product designs that align with consumer expectations for environmentally-friendly solutions.
Consumer Education on Battery Disposal Options
Educating consumers about proper battery disposal options is essential in mitigating the environmental impact of lithium batteries. Many individuals are often unaware of the local regulations or resources available for recycling batteries safely. By providing resources on where and how batteries can be disposed of responsibly, manufacturers and advocacy groups can play a crucial role in minimizing battery waste in landfills.
Furthermore, promoting awareness about the hazards associated with improper disposal will help cultivate a more responsible consumer base. As awareness grows, individuals may be more inclined to engage in programs that support recycling efforts. This collective effort can significantly reduce the environmental footprint caused by battery waste, creating a healthier planet for future generations.
Advancing Battery Technology: A Call for Sustainable Practices
As we advance into a future heavily reliant on battery technology, the call for sustainable practices becomes more urgent than ever. Stakeholders across the industry must work together to ensure that the surge in battery consumption does not equate to an increase in environmental harm. Strategies to improve manufacturing processes, design for disassembly, and prioritize recyclable materials should become industry standards.
Innovations in the fabrication of lithium batteries should also focus on minimizing toxic materials and enhancing energy efficiency. By adopting these practices, manufacturers not only can meet consumer demands but can also contribute to a healthier ecosystem. The interplay between performance, longevity, and environmental responsibility will become the defining factor for the future of battery technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are lithium batteries and how do they work?
Lithium batteries are rechargeable batteries that utilize lithium-ion technology to store and release electrical energy. They work by moving lithium ions between the anode and cathode during discharge and charge cycles, providing high energy density and efficiency. This makes them ideal for a variety of applications, from smartphones to electric vehicles.
Are lithium-ion batteries better than traditional rechargeable batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries generally offer better performance than traditional rechargeable batteries, such as nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. They provide higher energy density, lighter weight, and longer lifespan, making them suitable for portable electronics and electric vehicles. However, the choice depends on specific use cases and devices.
What is the environmental impact of lithium batteries?
The environmental impact of lithium batteries is a complex issue. While they help reduce fossil fuel dependence in electric vehicles, mining for lithium can result in ecological damage and water scarcity. Proper battery disposal and recycling are crucial to minimize these environmental effects and ensure sustainable practices in battery production and usage.
How should I dispose of lithium batteries?
Lithium batteries should not be thrown in regular trash due to their potential environmental hazards. Instead, they should be disposed of at designated battery recycling locations. Many electronic stores and recycling centers offer safe disposal options, ensuring that hazardous materials are handled properly and do not end up in landfills.
What is the ‘Right to Repair’ in relation to lithium batteries?
The ‘Right to Repair’ refers to the movement advocating for consumers’ ability to repair their electronic devices, including those powered by lithium batteries. It emphasizes the importance of access to spare parts and manuals so that products can be easily fixed, reducing waste and prolonging device lifespan, particularly for gadgets that use non-removable lithium-ion batteries.
Can I replace the lithium battery in my device easily?
Replacement of lithium batteries depends on the device design. Some devices have removable lithium batteries, making replacements straightforward. However, many modern electronics are designed with non-removable batteries, which complicates the process and often requires professional service. This issue underscores the importance of the Right to Repair.
What are the benefits of using lithium-ion technology in batteries?
Lithium-ion technology offers numerous benefits, including high energy density, lightweight construction, low self-discharge rates, and the ability to withstand numerous charge and discharge cycles. These characteristics make lithium batteries particularly effective for applications from consumer electronics to electric vehicles.
Are there alternatives to lithium batteries that are more sustainable?
Yes, there are alternatives to lithium batteries, such as solid-state batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and newer technologies like flow batteries, which aim to minimize environmental impact. However, currently, lithium-ion technology remains the most widely used due to its performance and cost-effectiveness.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The rise of affordable lithium batteries has transformed modern life, making devices more convenient compared to older battery technologies like AA. |
| Ian Bogost questions the assumption that lithium batteries are superior for every device. |
| Historical context: NiMH-based electric vehicles had limitations like short ranges in the 90s compared to lithium technology today. |
| Rechargeable lithium batteries lead to concerns about disposability and waste, particularly for less frequently used devices. |
| Bogost critiques the belief that all rechargeable batteries are inherently better without acknowledging improvements in NiMH technology. |
| Standardized lithium cells like the 18650 are popular due to their availability and efficiency. |
| The lack of easily replaceable batteries in many consumer electronics is a growing concern. |
| Potential future regulations might push for better battery options in consumer electronics. |
| Proper management of lithium-ion batteries is crucial due to their high power density and associated risks. |
Summary
Lithium batteries play a crucial role in enhancing our daily lives with their convenience and efficiency. Despite their advantages, there are ongoing discussions about whether they are the best choice for all devices. Critiques highlight the importance of considering alternatives and the implications of disposability associated with modern electronics. As regulations evolve, there may be a push toward more sustainable and easily manageable battery options, underscoring the importance of responsible battery use.